

A hydrophobic filter membrane acts as a crucial sterile barrier by blocking liquids and microbes while allowing air to pass freely. These membranes serve as both vent filters and moisture barriers in sterile vent barriers, protecting sensitive contents from contamination. PTFE remains a popular material choice because of its excellent resistance properties. Advanced manufacturing, such as the hollow fiber spinning machine, produces membranes with consistent pore structure. This technology helps maintain sterility and ensures product safety throughout storage and transport.
Hydrophobic filter membrane sets a new standard for secure, sterile packaging in demanding environments.
Key Takeaways
- Hydrophobic filter membrane blocks liquids and microbes while allowing air to pass, creating a strong sterile barrier that protects packaging from contamination.
- Advanced manufacturing with hollow fiber spinning machine ensures membranes have uniform pore size and structure, improving filtration efficiency and reliability.
- The membrane maintains airflow and pressure balance in packaging, preventing damage during storage and transport even in high humidity.
- PTFE-based hydrophobic membranes offer excellent chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for medical, pharmaceutical, and food packaging applications.
- Choosing the right hydrophobic membrane involves considering pore size, material compatibility, and quality standards to ensure long-term sterility and moisture protection.
How Does It Work?
Hydrophobic Filter Membrane Mechanism
A hydrophobic filter membrane operates by repelling water and resisting wetting at the molecular level. The surface of these membranes features a high intrinsic contact angle, which means water droplets bead up and roll off instead of soaking in. This property results from low surface energy materials, such as PTFE, which is widely used for its strong water repellency and chemical inertness. The hollow fiber spinning machine plays a crucial role in manufacturing these membranes, ensuring a consistent pore structure and high-quality performance.
| Mechanism Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Liquid Entry Pressure (LEP) | Minimum pressure needed for liquid to enter membrane pores, calculated by Young-Laplace equation. High LEP means better wetting resistance. |
| Intrinsic Contact Angle (θ_Y) | Higher θ_Y means stronger water repellency. |
| Surface Energy | Low surface energy repels water molecules. |
| Pore Size and Distribution | Smaller, uniform pores increase LEP and reduce wetting risk. |
| Hierarchical Porous Structure | Nano- and micro-scale roughness enhances repellency and vapor transport. |
| Surface Chemistry | Hydrophobic groups create a molecular barrier, allowing vapor passage but blocking water. |
| Experimental Evidence | Nanofilament-coated membranes show 30-60% higher distillation flux and improved wetting resistance. |
PTFE membranes, especially those produced with hollow fiber spinning machine, combine a nodal-fibrillar structure and controlled pore size. This design provides high porosity and permeability while maintaining filtration efficiency. The smooth, non-stick surface of PTFE also reduces fouling and microbial buildup, supporting long-term barrier performance.
Airflow and Pressure Equalization
Hydrophobic filter membrane allows air to pass freely while blocking liquids. This feature enables pressure equalization in sterile packaging, preventing package deformation or rupture during transport and storage. The precise control of pore size and structure, achieved through modern manufacturing methods, ensures reliable airflow rates and water entry pressure.
- Track-etched hydrophobic membranes offer high resistance to pressure changes, making them ideal for pressure equalization.
- Membranes can be tuned for specific airflow rates and water entry pressures, supporting a wide range of sterile venting needs.
- Self-cleaning and reversible flow properties enhance reliability in venting applications.
| Membrane Type | Pore Size Range (µm) | Airflow Rate (l/h/cm² @ 70 mbar) | Water Entry Pressure (mbar) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porex Virtek® PTFE Sintered | 0.22 – 50 | 0.25 – 70 | 10 – 800 |
| Porex Expanded PTFE Hydrophobic | 0.1 – 50 | 12 – 312 | 50 – 5000 |
Hydrophobic membrane maintains stable airflow even in high-humidity environments. Superhydrophobic modifications, such as methyltrimethoxysilane treatment, create surfaces with water contact angles above 90°, causing water droplets to bead and roll off. This non-wetting behavior protects the membrane structure from moisture damage and ensures high particulate removal efficiency, even when humidity reaches 90% or higher.
Blocking Liquids and Microbes
Hydrophobic filter membrane blocks both liquids and microbial contaminants through a combination of size exclusion and adsorption. Smaller pore sizes enhance the blocking of liquids and microbes by physically sieving particles and by adsorptive sequestration, where particles adhere to pore walls. For example, membranes with pore sizes around 0.22 µm can achieve microbial retention efficiencies up to 99.9995% in bacterial aerosol challenge tests. These filters effectively block bacteria such as Brevundimonas diminuta and Bacillus subtilis spores.
Hydrophobic filter membrane also demonstrates high efficiency in blocking viruses. Chemically modified membranes enhance both hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions, achieving virus removal rates up to 4.6 log reduction values. Pleated hydrophobic membrane filters retain over 99.999% of bacterial and viral contaminants, outperforming electrostatic filters, especially under high humidity or liquid challenge conditions.
PTFE’s biocompatibility and chemical inertness further reduce protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion, minimizing contamination risks. The smooth, low-friction surface of PTFE supports self-cleaning, reducing fouling and maintaining the microbial barrier function over time.
Tip: For optimal sterile packaging, select hydrophobic filter membrane manufactured with hollow fiber spinning machine. This ensures consistent pore size, superior hydrophobicity, and reliable microbial protection.
Benefits
Sterility Maintenance
Hydrophobic filter membrane provides a robust sterile barrier in packaging systems. The membrane prevents microbial ingress by repelling water and blocking the passage of bacteria and viruses. The unique surface tension properties of hydrophobic membranes ensure that water and contaminants cannot penetrate unless exposed to pressures far above normal storage conditions. This feature makes them highly effective as sterile vent barriers, especially in environments where maintaining sterility is critical.
A study on bioreactor design demonstrates that hydrophobic filter membrane with specialized connectors maintains sterility over extended periods. The membrane allows essential gas exchange while preventing liquid and microbial contamination, creating optimal conditions for sensitive products. In contrast, electret filters can lose efficiency under high temperature and humidity due to charge decay, which highlights the importance of choosing the right filter type and storage environment for long-term sterility.
Hydrophobic filter membrane outperforms hydrophilic and polycarbonate membranes in preventing microbial ingress. Hydrophilic membrane allows water to wet the surface and block air flow, making them less suitable for venting. Polycarbonate membranes permit liquid breakthrough at lower pressures. Hydrophobic membrane filters, such as those made from PTFE, maintain high water entry pressure and superior microbial barrier properties. This performance ensures that packaging remains sterile throughout storage and transport.
Hydrophobic filter membrane serves as a reliable viral barrier, protecting products from both bacterial and viral contamination.
Moisture Barrier
Hydrophobic filter membrane act as effective moisture barriers, protecting packaged products from humidity and water vapor. The structure of these membranes, often produced using a hollow fiber spinning machine, prevents water from entering the pores unless subjected to high pressure. This property keeps the interior of the package dry, which is essential for products sensitive to moisture.
The water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) of hydrophobic filter membrane, such as parylene C coatings, measures only 15.2 g m⁻² day⁻¹ under standard conditions. This low WVTR demonstrates excellent moisture barrier performance. By blocking moisture ingress, these membranes help extend product shelf life and reduce the risk of moisture-induced degradation.
PTFE membranes, known for their hydrophobicity, are widely used in venting applications and vacuum pump line protection. Their ability to repel water and prevent moisture entry supports product integrity over time. However, maintaining the hydrophobic state is crucial, as exposure to low surface tension fluids can compromise the barrier function.
| Membrane Type | WVTR (g m⁻² day⁻¹) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Parylene C | 15.2 | Superior moisture barrier |
| Parylene N | Higher than C | Most permeable among tested parylenes |
| Parylene AF4 | Not specified | Hydrophobic surface, high contact angle |
Chemical Resistance
Hydrophobic filter membrane, especially which made from PTFE, offers exceptional chemical resistance. The membrane withstands exposure to strong acids, bases, and solvents, making them suitable for harsh chemical environments. PTFE membranes maintain their structure and filtration efficiency even after repeated sterilization cycles, with thermal durability ranging from -200 ℃ to 260 ℃.
A comparison between PTFE and PVDF membranes shows that PTFE provides superior resistance to aggressive chemicals and higher thermal stability. While PVDF membranes offer greater mechanical strength, PTFE membranes excel in environments where chemical exposure and high temperatures are common. This resilience ensures that the sterile barrier remains intact, even during exposure to sterilizing agents or process chemicals.
| Chemical Agent | PTFE Membrane Resistance |
|---|---|
| Potassium Hydroxide, 3 N Caustic | Excellent |
| Sodium Hydroxide, 3 N Caustic | Excellent |
| Concentrated Sodium Hydroxide | Excellent (with some exceptions) |
Hydrophobic filter membrane resists fouling and clogging, ensuring consistent performance in corrosive and moisture-prone environments. The chemical inertness and hydrophobicity contribute to longer service life and reliability, supporting the growing demand for robust filtration solutions in industrial and pharmaceutical settings.
Tip: For applications requiring both a sterile barrier and chemical resistance, select hydrophobic membrane filters manufactured with hollow fiber spinning machine for optimal performance.
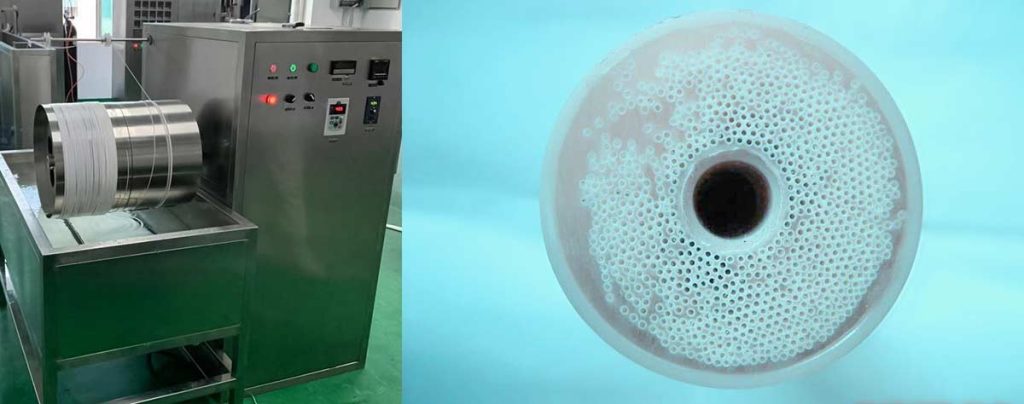

Membrane Filter Types
Microporous Hydrophobic Membranes
Microporous hydrophobic membranes play a vital role in sterile packaging. These membranes feature a network of uniform or nonuniform pores, designed to allow vapor transport while blocking liquid entry. Manufacturers often use PTFE, PVDF, or polypropylene to create these membranes, applying hydrophobic surface treatments to enhance water repellency. The hollow fiber spinning machine enables precise control over pore size and structure, resulting in reliable performance for sterile venting.
The typical pore size range for microporous hydrophobic membranes used in sterile packaging spans from 0.05 to 0.45 microns. This range ensures effective microbial retention and airflow. The following chart illustrates common pore sizes:
These membranes excel at blocking contaminants above their pore size, making them ideal for applications that demand both sterility and breathability.
Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic membranes differ in their surface properties and performance. Hydrophobic membranes repel water, allowing air and gas to pass while blocking liquids. This property makes them suitable as vent filters in sterile packaging. Hydrophilic membranes, on the other hand, absorb water easily and require pre-wetting for filtration of aqueous solutions. They often block air or gas flow when wetted, which limits their use in venting applications.
- Hydrophobic membranes maintain stable performance under sterilization and resist liquid penetration.
- Hydrophilic membranes offer better antifouling properties and higher permeability for aqueous solutions but are less effective for gas filtration.
Both membrane types with pore sizes of 0.45 microns or smaller can block bacteria such as E. coli and enterococcus. However, hydrophobic membranes provide superior protection against liquid ingress, which is critical for sterile packaging.
Traditional Filters Comparison
Traditional filters, such as granular or micron-level materials, offer low cost and resistance to high temperatures. However, they struggle with low filtration efficiency for fine particles and high air resistance. In contrast, a membrane filter made from microporous hydrophobic membranes maintains airflow and reliably retains microbes. The table below compares key aspects:
| Aspect | Microporous Hydrophobic Membranes | Other Filter Types (Hydrophilic, Polymeric, Inorganic) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Microporous, uniform or nonuniform pores; designed for vapor transport and liquid retention | Hydrophilic membranes wet easily; inorganic membranes strong but brittle |
| Surface Property | Hydrophobic, resists wetting, high liquid entry pressure | Hydrophilic, easily wetted; some repel water but allow low surface tension fluids |
| Application | Membrane distillation, gas filtration, sterile packaging | Hydrophilic for aqueous solutions; inorganic for harsh conditions |
| Manufacturing | Phase inversion, stretching, electrospinning, hollow fiber spinning machine | Polymeric easier to make; inorganic costly and brittle |
| Performance | High microbial retention, stable airflow | Polymeric limited by pH, temperature, pressure; inorganic fragile |
Tip: For sterile packaging, microporous hydrophobic membranes produced with a hollow fiber spinning machine deliver superior microbial retention and airflow compared to traditional filters.
Applications
Medical Packaging
Hydrophobic filter membrane plays a critical role in medical packaging. The membrane serves as vent filter in a wide range of medical device applications, ensuring sterility by blocking microbial ingress while allowing air and gas exchange. Manufacturers design these membranes to fit various shapes and sizes, meeting the specific needs of medical devices. Common uses include venting in inhalers, nebulizers, and spray pumps, where controlled airflow and contamination prevention are essential. The membrane also provides oil barrier functionality and protects against solvents with surface tension above 25 dynes/cm. Their compatibility with sterilization methods such as autoclaving, ethylene oxide, gamma, and e-beam supports safe and reliable packaging. The hollow fiber spinning machine enables precise control over membrane structure, enhancing performance in demanding healthcare environments.
- Venting for medical devices to maintain sterility
- Air and gas filtration that repels water and oils
- Customizable shapes and sizes for diverse packaging needs
Hydrophobic membranes in medical packaging help maintain product integrity and patient safety by preventing microbial contamination.
Pharmaceutical Use
Pharmaceutical manufacturing and packaging rely on hydrophobic filter membrane to maintain sterile conditions. The membrane repels water and resists wetting, making it ideal as vent filter for tanks, containers, and electrical enclosures. The membrane protects vacuum pumps from water aspiration and prevent contamination during air or gas filtration. By controlling bioburden and blocking microbial entry through air pathways, hydrophobic membranes support strict sterility standards. The water-repellent properties ensure reliable venting without water blockage, unlike hydrophilic membranes that can become wetted and block airflow. The hollow fiber spinning machine allows for consistent pore size and structure, which is vital for pharmaceutical packaging that demands both moisture barriers and dependable air filtration.
- Vent filters for tanks and containers
- Protection for sensitive equipment from water intrusion
- Reliable air and gas filtration to maintain sterility
Food Packaging
Food packaging benefits from hydrophobic filter membrane by reducing spoilage and contamination. The membrane physically removes microorganisms, lowering microbial load and extending shelf life. Manufacturers validate their effectiveness through microbial retention tests, achieving significant log reduction values. Hydrophobic films inspired by natural surfaces, such as swan feathers, create high water contact angles that minimize moisture contact and inhibit microbial growth. Materials like polydimethylsiloxane and LDPE with curcumin enhance moisture resistance and enable real-time spoilage detection. Multilayer films with hydrophobic outer layers regulate humidity, preventing both moisture loss and microbial growth. Active packaging with hydrophobic and antimicrobial features, such as chitosan-based polymers, further extends the freshness of foods like strawberries and shrimp. The use of biodegradable materials supports sustainability while maintaining food quality.
- Moisture regulation to prevent microbial growth
- Active packaging with antimicrobial and hydrophobic properties
- Shelf-life extension for fresh produce and seafood
Hydrophobic filter membrane in food packaging combines barrier protection and intelligent monitoring, supporting both food safety and environmental goals.
Selection Tips
Choosing the Right Membrane Filter
Selecting the right hydrophobic filter membrane for sterile packaging involves several important criteria. The filter must repel water while allowing gases and certain solvents, such as alcohol, to pass. This makes hydrophobic membranes suitable for sterilizing solutions containing alcohol or for use as air filters. Users should consider the following factors:
- Volume capacity and maximum pressure tolerance of the filter
- Compatibility with the material being filtered, including adsorption characteristics
- Nature of the filtered material, since viscous substances may require heating
- Surfaces in contact with sterilized products must remain pyrogen-free
- Stringent depyrogenation conditions may require separate processing steps
Pore size selection remains critical. A 0.22 μm membrane removes over 99.99% of bacteria, meeting sterilization standards. Bubble point testing verifies membrane integrity and directly relates to pore size. Hydrophobic membranes, such as those made from PTFE using a hollow fiber spinning machine, offer reliable performance for gas filtration and moisture barrier applications.
Quality and Standards
International quality standards play a vital role in the selection and use of hydrophobic filter membrane. Standards like ISO 9000 ensure that manufacturers produce filters under certified Quality Management Systems. This guarantees sterility assurance, high flow rates, and throughput, which are essential for sterile packaging. Each membrane undergoes integrity testing, such as bubble point and nitrogen diffusion tests, and comes with a Certificate of Quality for traceability and regulatory compliance. Material choice, such as PVDF for chemical resistance, must meet these standards. Filters must also withstand sterilization methods, including steam-in-place cycles, to ensure compatibility with packaging processes. Adhering to these standards ensures that the membrane provides consistent quality and meets industry regulations.
Manufacturing Technology
Manufacturing technology directly impacts membrane performance and reliability. The hollow fiber spinning machine enables precise control over pore size and structure, resulting in membranes with uniform properties. This technology supports the production of membranes that maintain high retention efficiency and integrity under various operating conditions. Manufacturers use advanced validation protocols, including microorganism challenge and bubble point tests, to confirm membrane performance. The choice of membrane material, combined with modern manufacturing techniques, ensures that the filter meets the strict requirements of sterile packaging and delivers consistent quality.
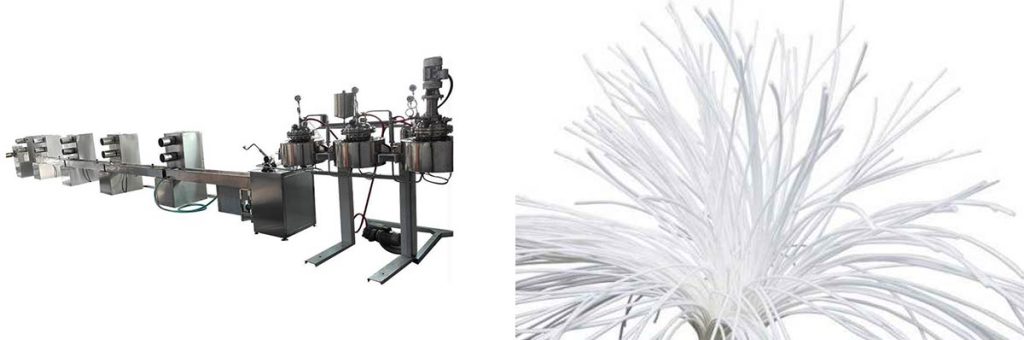
Conclusion
Hydrophobic filter membrane delivers unmatched protection for sterile packaging. The membrane provides a strong viral barrier, resist fouling, and support reliable performance in medical device applications. Recent studies show that both hydrophilic PVDF and PES filters achieve high bacterial retention, but optimal membrane selection and permeation rates remain crucial for minimizing protein loss.
| Filter Type | Protein Fouling | Bacterial Retention |
|---|---|---|
| PVDF (Hydrophilic) | Lower | High |
| PES (Hydrophilic) | Higher | High |
Manufacturers who choose advanced membranes made with hollow fiber spinning machine ensure the highest standards of safety and product integrity.
FAQ
What Makes Hydrophobic Filter Membrane Essential for Sterile Packaging?
Hydrophobic filter membrane blocks liquids and microbes while allowing air to pass. This function creates a strong viral barrier. Manufacturers use advanced methods like the hollow fiber spinning machine to ensure consistent quality and performance in sterile packaging.
How Do Hydrophobic Membranes Support Medical Device Applications?
Hydrophobic membranes maintain sterility in medical device applications by preventing microbial ingress. They allow controlled airflow, which protects sensitive equipment and supports safe operation in healthcare environments.
Can Hydrophobic Filter Membranes Withstand Chemical Exposure?
PTFE-based hydrophobic membranes resist strong acids, bases, and solvents. This chemical resistance ensures reliable performance during sterilization and in harsh environments, making them suitable for pharmaceutical and medical device applications.
What Role Does the Hollow Fiber Spinning Machine Play in Membrane Production?
The hollow fiber spinning machine creates membranes with uniform pore size and structure. This precision improves filtration efficiency and ensures each membrane meets strict industry standards for sterile packaging.
How Do Hydrophobic Membranes Provide a Viral Barrier?
Hydrophobic membranes use small, uniform pores to block viruses and bacteria. This design forms an effective viral barrier, which protects products from contamination during storage and transport.
